For appointment and information, you can rich us on +90532 433 6003(whatsapp)
 Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Genital Esthetic Surgeon in Turkey
Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Genital Esthetic Surgeon in TurkeyFor appointment and information, you can rich us on +90532 433 6003(whatsapp)
 Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Genital Esthetic Surgeon in Turkey
Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Genital Esthetic Surgeon in Turkey
Perinatology is the term used to describe the follow-up and management of pregnancies that are affected by high risk situations related to the pregnant patient or the fetus.

Increased blood pressure during pregnancy is a high risk life threatening condition both for the mother and the baby.
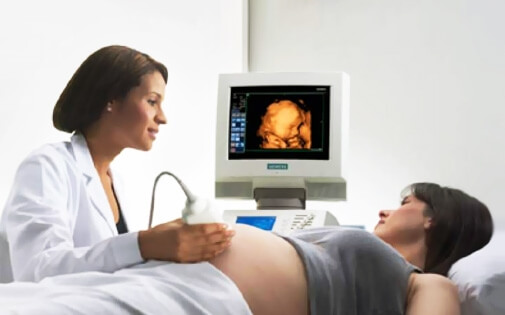
3D ultrasonography shows still pictures of the baby, whereas 4D ultrasonography reveals the baby live so that the parents can watch fetal movements such as kicking, thumb sucking, swallowing and even fascial expressions.

Gestational diabetes is the transient state of insulin resistance during pregnancy which leads to increased blood sugar levels.

For those patients who would like to give birth in Ankara, pregnancy follow-up is made by Dr. Burcu Saygan Karamürsel who is a perinatologist in our private clinic and 4 D ultrasound examination is performed at every antenatal visit.







It seems like you're asking about obstetrics Turkey. Obstetrics is a branch of medicine that focuses on pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. In Turkey, as in many other countries, obstetric care is an essential part of the healthcare system.
In Turkey, obstetric services are provided by obstetricians and gynecologists, who are medical doctors specialized in women's reproductive health. They play a crucial role in prenatal care, delivery, and postnatal care. The healthcare system in Turkey generally offers a range of services related to pregnancy and childbirth, including routine check-ups, prenatal screenings, and assistance during labor and delivery.
Public and private hospitals, as well as clinics, provide obstetric services in Turkey. The quality of care may vary, and individuals often have the option to choose between public and private healthcare facilities based on their preferences and financial capabilities.
You have been expecting to become pregnant for a while. Congratulations, your pregnancy test is positive. Most probably you made a home urine test to check if you are pregnant.
But you need to see an obstetrician to make sure that you are pregnant. A positive pregnancy test does not necessarily mean that you have a healthy pregnancy. At your first visit, an ultrasound examination can show whether you have an intrauterine or ectopic pregnancy. It also gives information about the number of fetuses, whether it is a singleton or multiple pregnancy.
During the first visit, your doctor will take a detailed history from you, to determine any possible risk factors. You may be prescribed pronatal vitamins and several blood and urine tests may be done.
If you have a family history of certain single gene disorders, special genetic tests may be necessary to determine if your fetus is also carrying the same genetic mutation.These tests and genetic counselling should ideally be done before getting pregnant, if possible. If you and your partner are both carriers for the same autosomal recessive genetic syndrome, it maybe necessary to make a diagnostic test called CVS (chorionic villus sampling) to determine if the fetus also has this genetic syndrome.
For the screening of chromosomal abnormalities,ultrasonography and blood tests can be used. Chromosomal abnormalities termed as trisomy are the most common abnormalities, which are not genetically inherited but happen during meiotic division of sperm and oocytes due to non-disjunction. The screening tests for the detection of trisomy 21(Down syndrome),Trisomy 18, Trisomy 13 and Sex chromosomal abnormalities are designed to be done around 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
Double test combines ultrasonography findings with two hormones measured in maternal blood.Maternal bood cell free fetal DNA test, which is more sophisticated than double test has a detection rate over 99% for Trisomy 21, 18 and 13.
When the screening or ultrasonography shows that there is a high risk for trisomy, diagnostic tests such as CVS or amniocentesis can be offered for definitive diagnosis. Since these are invasive tests, they are not offered to low risk patients but they are only offered when the screening tests find a high risk for chromosomal abnormalities.
When the diagnostic test result shows that the fetus has a chromosomal abnormality, the family can be counselled about the option of termination of pregnancy.
Ultrasonography is a very efficient tool for the detection of fetal morphological problems. Targeted scan is usually performed around 20-22 weeks of pregnancy for t he detailed examination of fetal organs.Ultrasonography also can detect certain genetic markers for the screeing of chromosomal abnormalities.
All pregnant patients should be screened for the risk of gestational diabetes by taking a detailed history in the beginning of pregnancy. The following conditions are considered as high risk for developing gestational diabetes:
For high risk patients, a diagnostic blood test called oral glucose tolerance test can be made as early as possible during pregnancy. For low risk patients gestational diabetes screening or diagnostic tests can be performed around 24-28 weeks of pregnancy.
When the tests show that the patient has gestational diabetes, she needs to follow a regular diet and exercise programme. If the blood sugar profile can be kept within normal limits, these measurescan be enough until birth. Otherwise, when the blood sugar profile shows levels above the desired range, it may be necessary to start insulin treatment for meticulous blood sugar control.
Your doctor can measure your blood presure and weight at each visit. Your baby’s growth can be monitored by certain methods. Uterine fundal height measurement is the simplest method.However since most antenatal clinics have an ultrasound machine, fetal biometry (mesurement of fetal body parts) is commonly applied during an ultrasound examination at each antenatal visit. It is not necessary to make a fetal ultrasound examination at each antenatal visit for low risk patients.
Sticking to a healthy diet programme and regular exercise during pregnancy can decrease the risk of several pregnancy complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia and thromboembolism.
Most pregnant patients can exercise during pregnancy, brisk walking, swimming, pregnancy yoga and pilates are a few examples that can be recommended. However if there is a complication during pregnancy that makes exercising risky, your doctor may warn you against exercising.